Joint-preserving procedures on the upper ankle joint
Introduction to joint-preserving procedures for the ankle joint
The ankle joint plays a crucial role in mobility and everyday life, but is also susceptible to wear and tear and injuries. This can lead to conditions such as osteoarthritis or cartilage damage. Traditionally, ankle fusion (arthrodesis) was seen as a common solution for severe cases. However, modern advances in orthopaedic surgery allow for joint-preserving alternatives that preserve the function and mobility of the joint.
Three main procedures that contribute to the preservation of the ankle joint are distraction arthroplastythe osteotomy and cartilage and bone transplantation. These methods improve patient mobility and reduce pain without the limitations of joint stiffness.
Causes of ankle joint degeneration
Several factors contribute to the deterioration of the ankle joint:
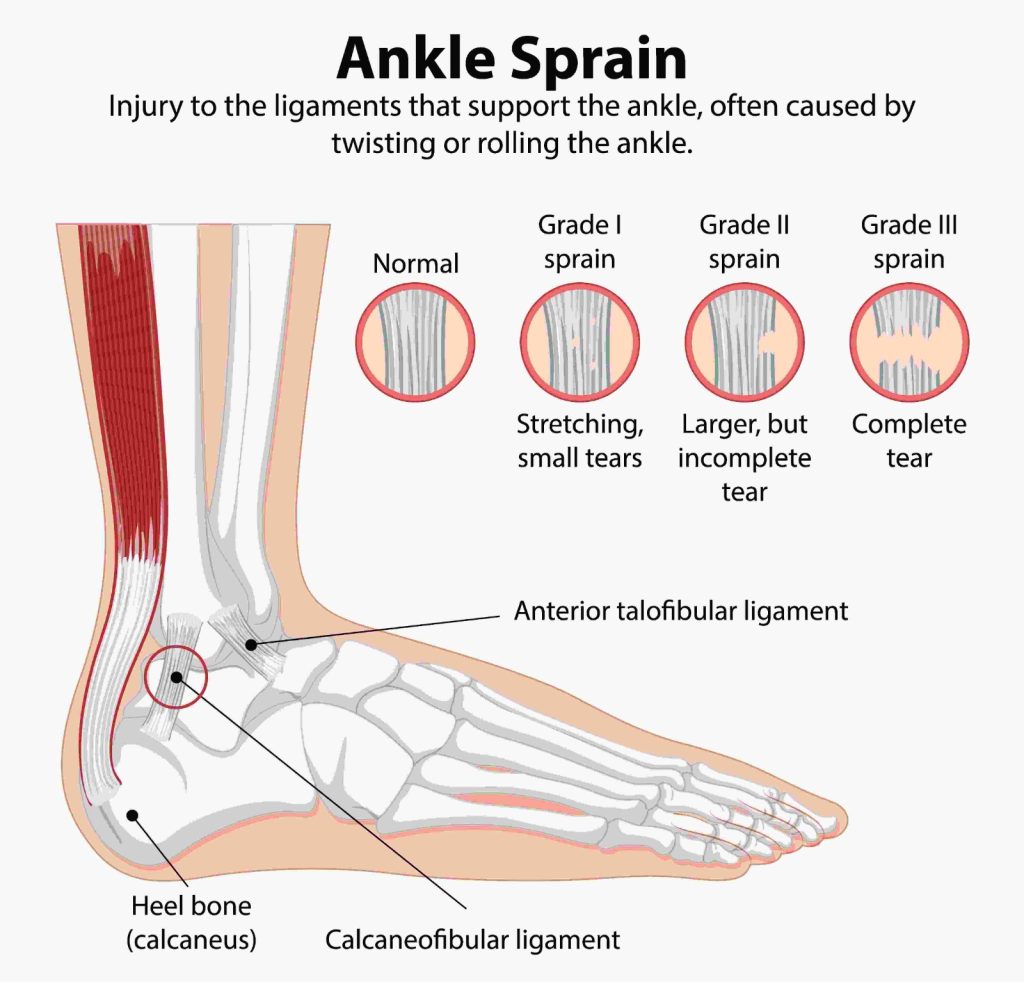
- Post-traumatic osteoarthritis - Injuries such as fractures or torn ligaments can lead to long-term instability and cartilage damage.
- Osteoarthritis - Progressive wear and tear of the joint cartilage over time.
- Inflammatory diseases - Diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis can accelerate joint degeneration.
- Congenital deformities - Malformations or developmental problems can lead to uneven loading of the ankle joint.
Early detection of these causes enables timely intervention and the use of joint-preserving treatment methods.
Treatment options for preserving the ankle joint
Distraction arthroplasty
Distraction arthroplasty is an innovative technique in which the joint surfaces of the ankle are temporarily separated using an external fixator. This allows the cartilage to regenerate and the pressure in the joint is redistributed, slowing down the wear and tear process.
Procedure of the treatment:
- Attachment of an external fixator for gentle distraction of the joint.
- Controlled movements and loads are encouraged during the recovery phase.
- After a few months, the fixator is removed and the joint remains in an improved condition.
Advantages:
- Preservation of the natural joint structure.
- Reduction of pain and inflammation.
- Delay or avoidance of joint fusion or joint replacement.
Cartilage and bone transplantation
For patients with localized cartilage damage, a cartilage and bone graft can restore joint integrity. In this technique, healthy cartilage is transplanted either from another part of the body or from a donor to replace damaged areas.
Types of transplants:
- Autograft - the patient's own cartilage is removed and reimplanted.
- Allograft - donor cartilage and bone are used to reconstruct the joint.
Advantages:
- Restoration of the damaged joint surface.
- Maintaining the mobility and function of the ankle joint.
- Long-term pain relief for cartilage loss.
Osteotomy
Osteotomy is a surgical procedure in which the bone is precisely cut and realigned to better distribute the body weight and reduce the pressure on the damaged joint. This technique is particularly suitable for patients with malalignment or uneven loading of the ankle joint.
Procedure of the treatment:
- The surgeon makes a precise bone incision to correct the deformity.
- The bone is repositioned to improve the load distribution.
- The new alignment is secured with plates, screws or other fixing methods.
Advantages:
- Restoration of the correct joint mechanics.
- Reduction of pain and slowing down of the degenerative process.
- Delaying or avoiding more invasive procedures such as joint fusion or replacement.
Advantages of joint-preserving procedures compared to fusion
While joint fusion effectively eliminates pain, it severely restricts mobility and significantly changes the gait pattern. Joint-preserving procedures, on the other hand:
- Maintain natural movement - enable a more normal gait pattern.
- Reduce the load on neighboring joints - Prevent accelerated wear of the knee and hip.
- Provide long-term benefits - delay or avoid the need for more invasive surgery.

Who are these procedures suitable for?
Suitable candidates for joint-preserving ankle treatments are:
- Patients with early to moderate osteoarthritis.
- People with cartilage damage or localized joint problems.
- Young and active patients who want to maintain their mobility.
- Patients who want to avoid the limitations of ankle fusion.
A thorough examination by an orthopaedic specialist determines the best course of action for each individual case.
Success rates and case studies
Clinical studies have shown that distraction arthroplasty, cartilage transplantation and osteotomy can significantly reduce pain and improve function. Many patients experience long-term relief and avoid joint fusion.
Case study: A 45-year-old athlete with incipient osteoarthritis underwent distraction arthroplasty. Within a year, he reported a 80% pain relief and a significant improvement in his daily activities, preventing stiffness.
Frequently asked questions
Recovery varies, but usually takes three months and involves gradual weight bearing and physiotherapy.
While the results are long-lasting, ongoing joint care and avoiding excessive strain on the ankle are essential to maintain the benefits.
Many patients return to low-impact activities. However, to maintain the health of their joints, strenuous sports may need to be limited.
You can arrange a consultation with me here to discuss your specific case.
Contact information
For more information or to make an appointment, book an appointment here or give us a call.