Joint-preserving knee surgery
Introduction to joint-preserving knee surgery
Knee joint pain and joint wear and tear are common problems that affect people of all ages. Many patients immediately think of a knee replacement if their symptoms persist. However, modern orthopaedic procedures offer numerous joint-preserving techniques that can significantly delay or even avoid the need for a total knee replacement. These include osteotomies (axis corrections), cartilage and bone transplants and meniscus transplants.
These surgical procedures aim to restore knee joint function while preserving as much of the natural joint structure as possible. Patients suffering from chronic knee pain due to malalignment, cartilage damage or meniscus defects can benefit from these procedures to improve their mobility and quality of life – without a total knee replacement.
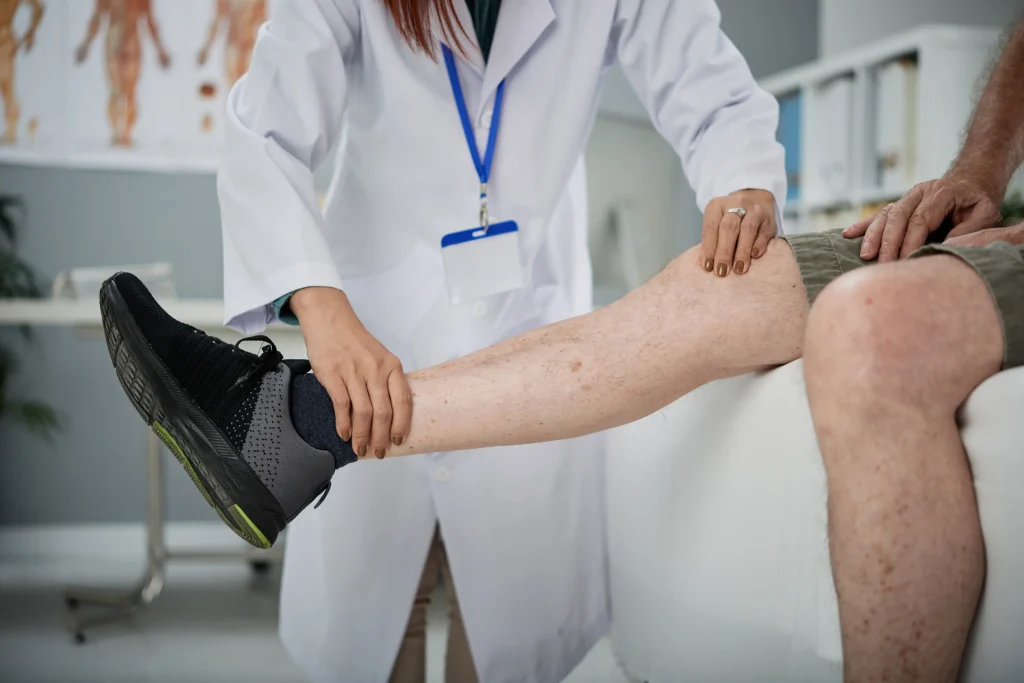
What is joint-preserving knee surgery?
Joint-preserving knee surgery involves various advanced orthopaedic procedures that correct structural problems and repair damaged tissue in the knee joint. In contrast to total knee replacement, in which the damaged joint is removed and replaced with a prosthesis, these operations focus on preserving and restoring the natural joint structures.
The most important procedures include
- Osteotomies - axial corrections to improve load distribution in the knee joint.
- Cartilage transplantation - procedure to repair cartilage damage and prevent further joint degeneration.
- Bone grafting - Transplantation of healthy bone tissue to restore the joint structure.
- Meniscus transplantation - replacement of a damaged or removed meniscus with a donor meniscus to restore knee joint function.
Osteotomies: Axial correction for long-term joint health
What is an osteotomy?
An osteotomy is a surgical procedure in which bones are cut and reshaped to correct misalignments. This technique is particularly beneficial for younger, active patients with early stages of osteoarthritis or joint deformities that lead to uneven cartilage wear.
Types of osteotomies
- High tibial osteotomy (HTO): Used to correct bow legs (varus deformity) in order to shift the load away from the damaged side of the joint.
- Distal femoral osteotomy (DFO): Correction of knock knees (valgus deformity) to distribute joint pressure more evenly.
Advantages of osteotomies
- Pain relief through better load distribution.
- Delaying or avoiding a knee replacement.
- Improved mobility and activity level for younger, active patients.
Cartilage and bone transplants
Cartilage transplantation
Cartilage transplantation is used to treat localized cartilage damage before it leads to more serious joint damage. The main techniques include:
- Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI): Removal of healthy cartilage cells from the patient, cultivation in the laboratory and reimplantation in the damaged area to regenerate the cartilage.
- Osteochondral autograft or allograft transplantation: Transplantation of healthy cartilage and bone tissue from an unaffected area of the body (autograft) or from a donor (allograft) into the damaged knee joint.
Bone grafting
Bone grafting is used in cases of significant bone loss, e.g. due to trauma, osteonecrosis or previous surgery. This procedure helps to restore the structural integrity of the knee and create a stable basis for cartilage repair.
Meniscus transplantation: My 25 years of experience
What is a meniscus transplant?
The meniscus plays a crucial role in the stability of the knee joint and shock absorption. If a meniscus is removed or severely damaged, the risk of cartilage wear and osteoarthritis increases considerably. Meniscus transplantation replaces the missing meniscus with a donor meniscus to restore joint function.
Who is a suitable candidate for a meniscus transplant?
- Patients under the age of 50 who have already had a complete or partial meniscectomy.
- People with persistent knee pain due to a meniscus deficiency.
- Patients without advanced osteoarthritis, as transplantation is most effective in the early stages of joint damage.
Advantages of meniscus transplantation
- Restoration of knee joint stability and function.
- Prevention of further cartilage damage and joint wear and tear.
- Reduced risk of early development of osteoarthritis.
Success rates and case studies
Long-term clinical studies and patient histories confirm the high success rates of joint-preserving knee operations:
- Osteotomies significantly reduce knee pain and improve joint function with a success rate of over 80% after 10 years.
- Cartilage and bone transplants provide long-term pain relief and improved joint mechanics in over 80% of cases.
- Meniscus transplants have been shown to delay the progression of osteoarthritis and improve knee joint function in more than 85% of cases.
Frequently asked questions
The recovery time varies depending on the procedure. Osteotomies and meniscus transplants usually take 3-6 months, while cartilage and bone transplants can take around 4-6 months.
Suitable candidates are patients with early to moderate joint degeneration, knee instability, cartilage damage or meniscus deficits who wish to avoid a knee prosthesis.
General surgical risks include infections, blood clots and healing complications. However, with professional aftercare and rehabilitation, the risks are low.
The return to sporting activities depends on the procedure and the healing process. Light exercise is often possible after 4-6 months, while high-performance sport requires around 9 months.
Please do not hesitate to contact me for further information or a consultation in my practice in Vienna.